NCERT Solutions for Science Class 9 Chapter 6
Chapter 6: Tissues
Intext Questions:
Question 1: What is a tissue?
Answer: Tissue is a collection of cells with comparable structures that are placed in order to fulfil a given activity.
Question 2: What is the utility of tissues in multicellular organisms?
Answer: Tissues in multicellular organisms are differentiated to perform a specific function at a given location, a process known as division of labor. Nerve cells, for example, make up the neurological tissue that aids in message transmission, whereas muscular cells make up the muscle tissue and muscle tissue is a type of tissue that aids in movement.
Questio3: Name the types of simple permanent tissues
Answer: Parenchyma, Collenchymas, and Sclerenchyma are the three forms of simple permanent tissues. Aerenchyma and chlorenchyma are two types of parenchyma tissue.
Question 4: Where is apical meristem found?
Answer: At the growing tips of stems and roots, the apical meristem is present.
Question 5: Which tissue makes up the husk of coconut?
Answer: Sclerenchyma tissue which is a form of simple permanent tissue makes up thehusk of the coconut.
Question 6: What are the constituents of phloem?
Answer: The food-conducting tissue of plants is termed as phloem. Sieve tubes, Companion cells, Phloem parenchyma, and Phloem fibers are the four components.
Question 7: Name the tissue responsible for movement in our body.
Answer: Muscle Tissues are responsible for movement.
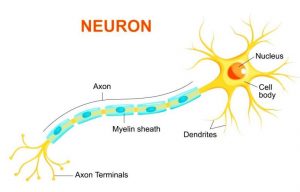
Question 8: What does a neuron look like?
Answer: A neuron is made up of three parts: the cell body, the axon, and the dendrites.
Dendrites are a significant number of extensions that stretch outward from the cell body and resemble branches. A nucleus and other cell organelles make up the cell body. An axon is a tube-like structure that transports an electrical impulse from the cell body to the neuron’s opposite end structures.
Question 9: Give three features of cardiac muscles.
Answer: Features of cardiac muscles:
● They are involuntary in nature.
● They are cylindrical, branched, and uninucleate in structure.
● Throughout their lives, they exhibit cyclic contraction and relaxation.
Question 10: What are the functions of areolar tissue?
Answer: Areolar tissues are commonly seen in animals. They are connective tissues that exist between the skin and the muscles. They can also be found in the bone marrow and around blood arteries and nerves. These tissues take up a lot of room inside the organs. They protect the internal organs and aid in tissue restoration in the event of harm.
EXERCISE
Question 1: Define the term “tissue”.
Answer: A tissue is described as a group of cells with identical structures that collaborate to execute a certain purpose.
Question 2: How many types of elements together make up the xylem tissue? Name them.
Answer: The xylem tissue is made up of four main elements as mentioned:
● Vessels
● Tracheids
● Xylem fibres
● Xylem parenchyma
Question 3: How are simple tissues different from complex tissues in plants?
Answer:
| Simple Tissue | Complex Tissues |
| Simple tissues consist of only one type of cell | They are comosed of various types of cells |
| The structures of all the cells are similar and they perform similar duties. | The roles and structures of different types of cells vary. |
| Plants have three types of simple tissues: parrenchyma, collecnchyma, and selerenchyam | Xylem and pholem are two types of complex permanent tissues found in plants. |
Question 4: Differentiate between parenchyma, collenchyma and sclerenchyma, on the basis of their cell wall.
Answer:
| Parenchyma | Collenchyma | Sclerenchyma |
| Thin cell walls, cells are loosely packed. | The cell wall is thickened irregularly at the corners, and there is very little space etween the cells. | There are no intercellular spaces because the cell walls are evenly thickened. |
| Cell wall is made up of cellulose. | Pectin and hemicellulose are the two most important components of the cell wall. | There is an extra layer of the cell wall that is mostly made up of lignin. |
Question 5: What are the functions of the stomata?
Answer: Stomata functions include the exchange of gases with the atmosphere. The stomata are responsible for transpiration.
Question 6: Diagrammatically show the difference between the three types of muscle fibres.
Answer: Striated muscles, smooth muscles (unstriated muscle fibre), and cardiac muscles are the three types of muscular fibres.
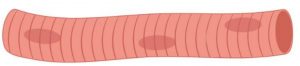
Striated Muscle cells
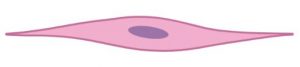
Smooth muscle cells
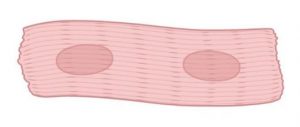
Cardiac muscle cells
Question 7: What is the specific function of the cardiac muscle?
Answer: The cardiac muscle is responsible for controlling the heart’s contraction and relaxation.
Question 8: Differentiate between striated, unstriated and cardiac muscles on the basis of their structure and site/location in the body.
Answer:
| Striated Muscles | Unstriated Muscles | Cardiac Muscles |
| On The Basis of Structure: | ||
| Cylinderical | Long | Cylinderical |
| Not branched | Not branched | Branched |
| Multinucleate | Uninucleate | Uninucleate |
| Its ends are blunt | Its ends are tapering | Its ends are flat and wacy |
| Coloured alternate light an dark bands | There are no bands present | Faint bands are present |
| On The Baseis of Location: | ||
| These muscles are present in different body parts such as hands, legs, tonue, etc. | The contraction and relaxation of blood vessels, as well as the movement of food in the alimentary canal, are all contrilled by these muscles. | These muscles control the heart’s contaction and relaxation. |
Question 9: Draw a labeled diagram of a neuron
Answer:
Question 10: . Name the following:
(a) Tissue that forms the inner lining of our mouth.
(b) Tissue that connects muscle to bone in humans.
(c) Tissue that transports food in plants.
(d) Tissue that stores fat in our body.
(e) Connective tissue with a fluid matrix.
(f) Tissue present in the brain.
Answer:
(a) Epithelial tissue
(b) Dense regular connective tissue (tendons)
(c) Phloem
(d) Adipose tissue
(e) Blood
(f) Nervous tissue
Question 11: Identify the type of tissue in the following: skin, the bark of a tree, bone, lining of kidney tubule, vascular bundle.
Answer:
● Skin: Stratified squamous epithelial tissue
● The bark of a tree: Simple permanent tissue
● Bone: Connective tissue
● The lining of kidney tubule: Cuboidal epithelial tissue
● Vascular Bundle: Complex permanent tissue
Question 12: Name the regions in which parenchyma tissue is present.
Answer: Leaves, fruits, and flowers.
Question 13: What is the role of the epidermis in plants?
Answer: Role of the epidermis:
● Protection of different parts of the plant.
● Epidermal cells present in roots, help in absorption of water.
● For protection against loss of water, mechanical injury, and parasitic fungus by producing a waxy, water-resistant covering called cuticle, which is made of cutin, on the outer surface of the plant.
Question 14: How does the cork act as a protective tissue?
Answer: The cork, which is made up of dead cells, is the bark of a tree. It protects the plant from mechanical damage and temperature extremes, as well as it prevents water loss through evaporation.
Question 15: Complete the table:
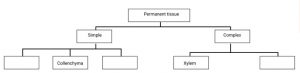
Answer: