Class-IX Social Science Geography Contemporary India -I Chapter 5: Natural Vegetation and Wildlife
1. Choose the right answer from the four alternatives given below:
i. To which one of the following types of vegetation does rubber belong to?
(a) Tundra
(b) Tidal
(c) Himalayan
(d) Tropical Evergreen
Ans: (d) Tropical Evergreen
ii. Cinchona trees are found in the areas of rainfall more than
(a) 100 cm
(b) 50 cm
(c) 70 cm
(d) less than 50 cm
Ans: (a) 100 cm
iii. In which of the following state is the Simlipal bio-reserve located?
(a) Punjab
(b) Delhi
(c) Odisha
(d) West Bengal
Ans: (c) Odisha
iv. Which one of the following bio-reserves of India is not included in the world network of bio-reserve?
(a) Manas
(b) Nilgiri
(c) Gulf of Mannar
(d) Panna
Ans: (d) Panna
2. Answer the following questions briefly:
i. Define an ecosystem.
Ans: One cannot separate the biotic elements from the abiotic elements from the environment. The interrelationship between these living and non-living components of the environment at any given place at a given time create a system that is known as an ecosystem.
ii. What factors are responsible for the distribution of plants and animals in India?
Ans: For the distribution of plants and animals in India, mainly climatic and relief factors are responsible.
Climate:
• Temperature: Vegetation of any place depends upon temperature and with vegetation, the animal species changes. Higher mountains have specific types of plants that are not found in the plains.
• Rainfall: Differences in annual rainfall or precipitation, changes the vegetation of a place thus animal types also change alongside it. Areas with heavy rainfall show denser vegetation and more animal diversity.
• Photoperiod: Availability of sunlight duration also changes the pattern of flora and fauna. The places with longer daylight have different vegetation compared to places with shorter daylight availability.
• Relief:
• Land: The natural vegetation alters with change in land type. The mountains, plains and plateau show different vegetation as per altitude, temperature, rainfall and soil nature.
• Soil: The soil nature changes along the higher mountain, plains and plateau area in India. Thus, we see different types of plants in these places. At the same time, animal types also change with it.
iii. What is a bio-reserve? Give two examples.
Ans: A bio-reserve can be defined as a protected zone where specific flora and fauna are conserved. Two examples of bio-reserve are— Sundarbans Biosphere Reserve and Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve.
iv. Name two animals having habitat in tropical and montane type of vegetation.
Ans:
• Two animals having habitat in tropical vegetation are—one-horned rhinoceros and Indian elephant.
• Two animals having habitat in montane vegetation are— Kashmir stag and spotted deer.
3. Distinguish between:
i. Flora and Fauna
Ans: The distinguishing features between flora and fauna are:
|
Flora
|
Fauna
|
|---|---|
|
All the plant species observed in a given place at a given time is known as the flora of that place.
|
All animal species observed in a given place at a given time are known as the fauna of that place.
|
ii. Tropical Evergreen and Deciduous forests
Ans: The distinguishing features between tropical evergreen forest and deciduous forest are:
|
Tropical evergreen forest
|
Deciduous forest
|
|---|---|
|
Tropical evergreen forest grows in areas with average annual rainfall over 200 cm followed by a short dry season.
|
Deciduous forest grows in areas with average annual rainfall between 70−200 cm.
|
|
Trees of these forests remain green throughout the year.
|
At a specific season, the trees drop all their leaves and stand bare.
|
|
Common trees of this forest are— ebony, mahogany, rosewood, rubber and cinchona, etc.
|
Common trees of this forest are— Teak, bamboo, sal, shisham, sandalwood, khair, kusum, arjun, mulberry, etc.
|
|
Common animals of this forest are— elephants, monkeys, lemurs, deer, birds, snakes, bats, sloths, scorpions, snails, etc.
|
Common animals of this forest are— lion, tiger, pig, deer and elephant, birds, lizards, tortoise, snakes etc.
|
4. Name different types of vegetation found in India and describe the vegetation of high altitudes.
Answer: The various types of vegetation found in India are noted below.
● Tropical evergreen forests
● Tropical deciduous forests
● Tropical thorn forests and scrubs
● Montane forests
● Mangrove forests
Vegetation of higher altitude:
The mountains show the declining temperature with the rise in altitude which constantly changes the vegetation in a natural progression.
• The regions at a height of 1000− 2000metres from sea level show wettemperate forests. Here species of oak, chestnut, etc. evergreen trees with broad leaves are found.
• The regions at a height of 1500−3000 metres from the sea level show temperate forests formed of coniferous trees such as pine, deodar, spruce, silver fir, cedar etc.
• At the higher altitude, i.e., regions over 3600 metres, the alpine vegetation is observed. The flora of such places is dominated by species of juniper, pine, birch, silver fir, etc.
• The height of these plants gets stunted as the altitude reaches the snowline. The trees there are mostly shrubs and scrubs which combine with the Alpine grasslands.
• At very high altitudes, mostly mosses and lichens are observed which form the tundra vegetation.
5. Quite a few species of plants and animals are endangered in India. Why?
Ans: The reasons behind different plants and animals being endangered in India are given below.
• Loss of habitat due to urbanisation and formation of industries.
• Deforestation in large areas to expand agricultural lands and residential areas.
• Pollution of soil, water and air.
• Illegal hunting and poaching in forests.
6. Why has India a rich heritage of flora and fauna?
Ans: The rich heritage of flora and fauna in India has grown due to the following reasons.
• The natural geographical diversity of India shows various relief features. The presence of mountains, plateaus, plains, and coastal areas has helped to develop different types of vegetation that support diverse species of animals.
• The soil type of various parts of India changes with the nature of the relief. Thus, vegetation along with animal species changes.
• Rainfall and temperature vary in different parts of the country, thus the vegetational variety is noticed in different regions of India. With the changes in floral dynamic, fauna diversity alters too.
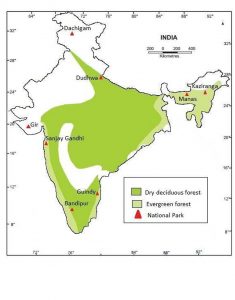
• The availability of sunlight during different seasons varies in India with the change of latitude. Thus, we observe a difference in vegetation and animals throughout the country. Map Skills On an outline map of India, label the following.
i. Areas of Evergreen Forests
ii. Areas of Dry Deciduous Forests
iii. Two national parks each in Northern, Southern, Eastern and Western parts of the country
Ans: The outline of India’s map is given below with the labelling of the above-mentioned areas.
Study materials
- Refernce Books
- NCERT Solutions
- Syllabus









